Acne
If acne is severe or deep, vigorous treatment is required to reduce scarring. For severe, deep lesions topical treatment is unsatisfactory. Consultation with your health professional is advised.
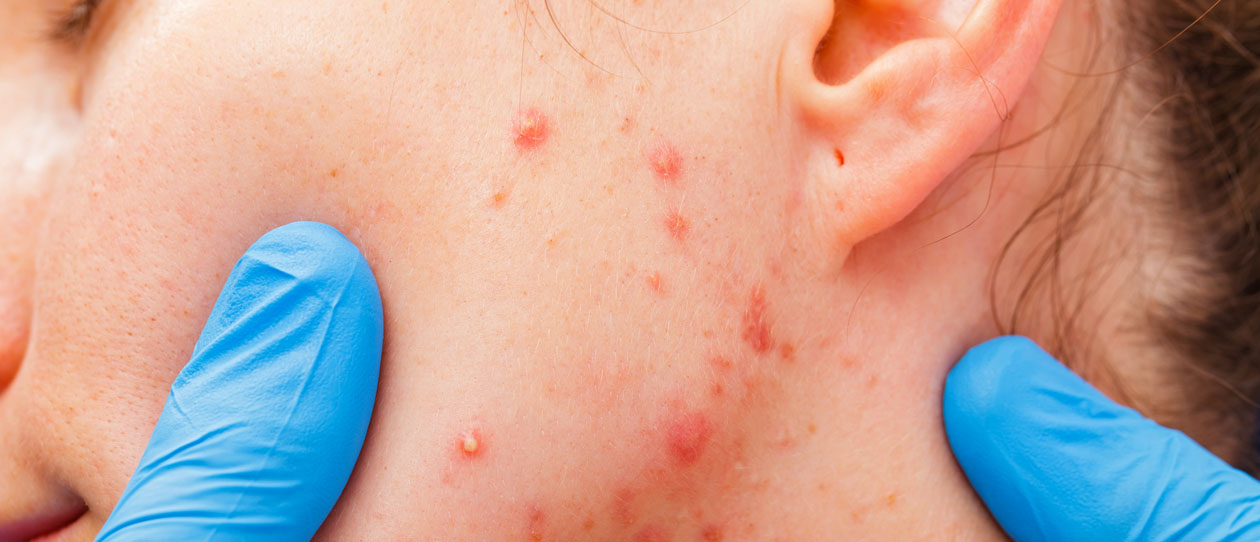
Symptoms
Acne vulgaris, the most common form of acne, consists of whiteheads, blackheads, pimples and deep cysts that appear mainly on the face and to a lesser extent on the chest, shoulders and back.
Acne is often worse during winter, improving during summer.
Causes
Acne commences when the sebaceous ducts in the skin become blocked by skin overgrowth to form a whitehead, or by plugs of sebum which darken on exposure to air forming a blackhead.
When the sebum trapped in the whitehead or blackhead is forced into the deeper skin layers, an inflammatory reaction causes a red lump called a papule. If infection follows, pus collects and the classic pimple (pustule) is seen. When the inflammatory condition is severe, large, painful cysts may form.
Acne is associated with hormonal imbalance, and will typically develop during puberty when hormonal activity increases the size and activity of the sebaceous glands. Some women also experience acne as a component of pre-menstrual syndrome.
The naturopathic view is that acne is aggravated by ineffective elimination from the body, which may be related to a build up of toxins in the system due to an inability of the liver to effectively break down circulatory toxins. It can also be initiated by food sensitivities, poor diet and stress.
Natural Therapies
Zinc is an essential mineral used for wound healing and the normal oil gland function of the skin. It is also involved in the maintenance of vitamin A levels, transport and usage; for protein synthesis, (particularly collagen synthesis); and to help maintain hormonal balance.
Beta-carotene is transformed into vitamin A in the body. These two nutrients act as skin antioxidants, and may be of assistance in the treatment of acne, other skin conditions, and the healing of wounds.
Sulphur is traditionally indicated as a liver tonic to support the body's detoxification processes, and for a variety of skin conditions including acne which are associated with sluggish liver function.
Echinacea has been extensively investigated and has been found to have a variety of actions on the immune system, including antibacterial and antiviral activity.
Calendula has traditionally been used for the treatment of skin infection and to assist wound healing.
Vitex Agnus-Castus is indicated for acne problems which are worse pre-menstrually.
Life Style Factors
Make sure your skin care regime includes twice daily cleansing, toning and moisturising. Products containing anti-bacterial herbs such as tea tree oil to reduce infection, are ideal. It is also important to maintain moisture balance using an oil-free moisturiser. A clay mask once a week will remove dirt and tighten pores.
Proper nutrition and skin cleanliness, together with adequate rest, fresh air and sunlight, are helpful in the treatment of acne.
Do not scrub the skin. Scrubbing stimulates growth of skin cells, aggravating the condition. Instead, try an antibacterial face wash. Choose oil-free cosmetics and ensure all makeup brushes and sponges are washed regularly. Keep your hands away from your face to avoid the spreading of acne.
Remedies
There are conflicting theories about direct dietary influences on acne. The best approach is to adopt a healthy well balanced diet high in fibre, filtered water and fresh fruits and vegetables. Avoid refined or processed foods, sugars and high-fat foods.
Regular exercise is great for your skin, as it improves your circulation and aids in the removal of toxins. Try brisk walking, jogging swimming or any active sport 3 - 4 times per week.
